AWS EC2 Instances Tutorial (Step 1 on 4)
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) is a web service that provides secure, resizable compute capacity in the cloud. It is designed to make web-scale cloud computing easier for developers. This tutorial will help you get jump started with AWS EC2.
1. Go to Amazon Web Services’ Website
The step one is simple, you need to go to AWS’ website.
Here i the link : AWS’ Website Click on “Sign In to the Console” (top right)
Then, you just to sign in if you have account, if not make one.
2. Launch EC2 instances
Now, click on “EC2” and then, you will have this page :
Click on “Launch Instance”. 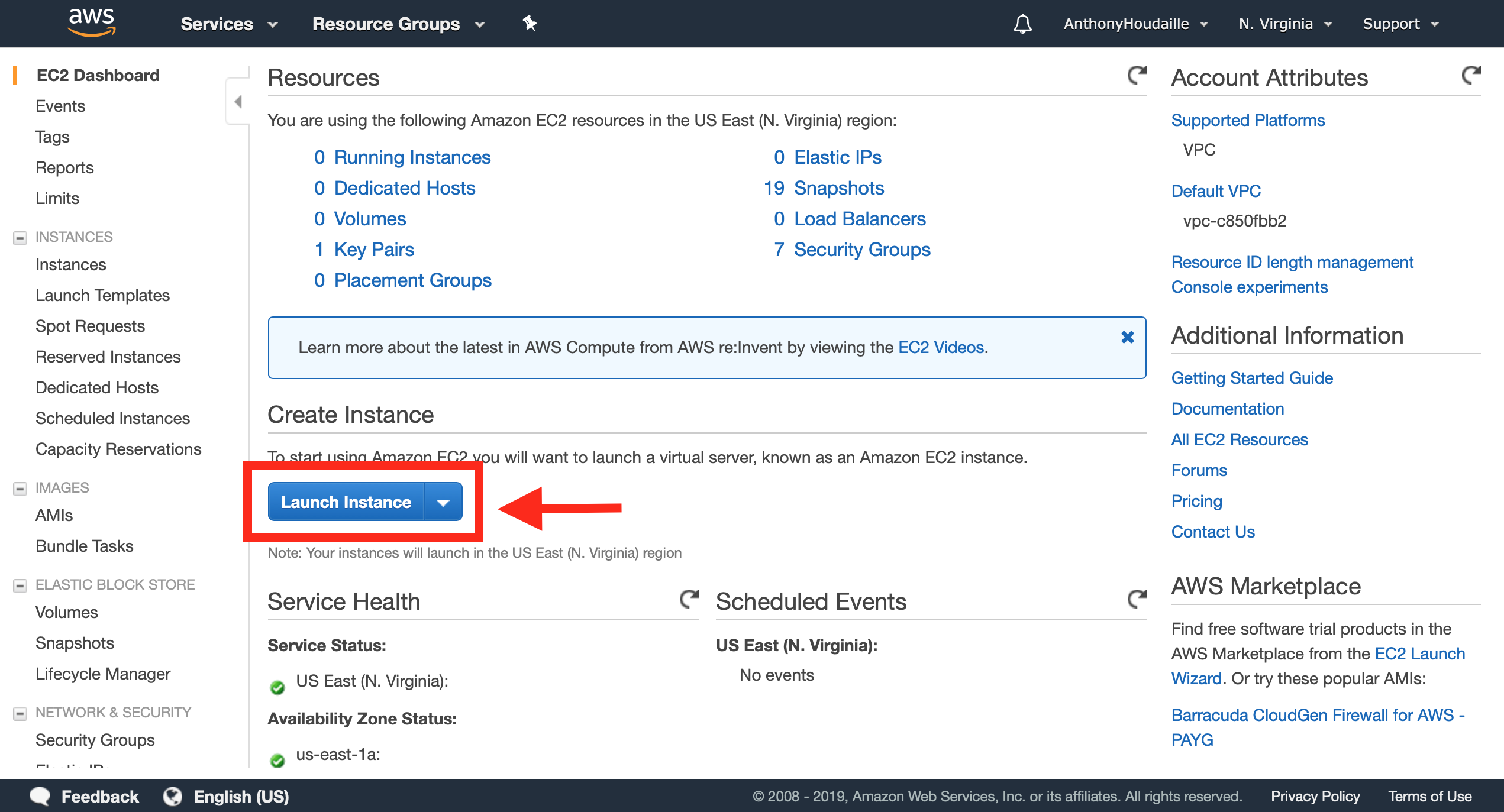
3. Choose your AMI
At this point, you will select the boot OS.
For this tutorial, I’ll choose “Ubuntu Server 18.04 LTS (HVM), SSD Volume Type” 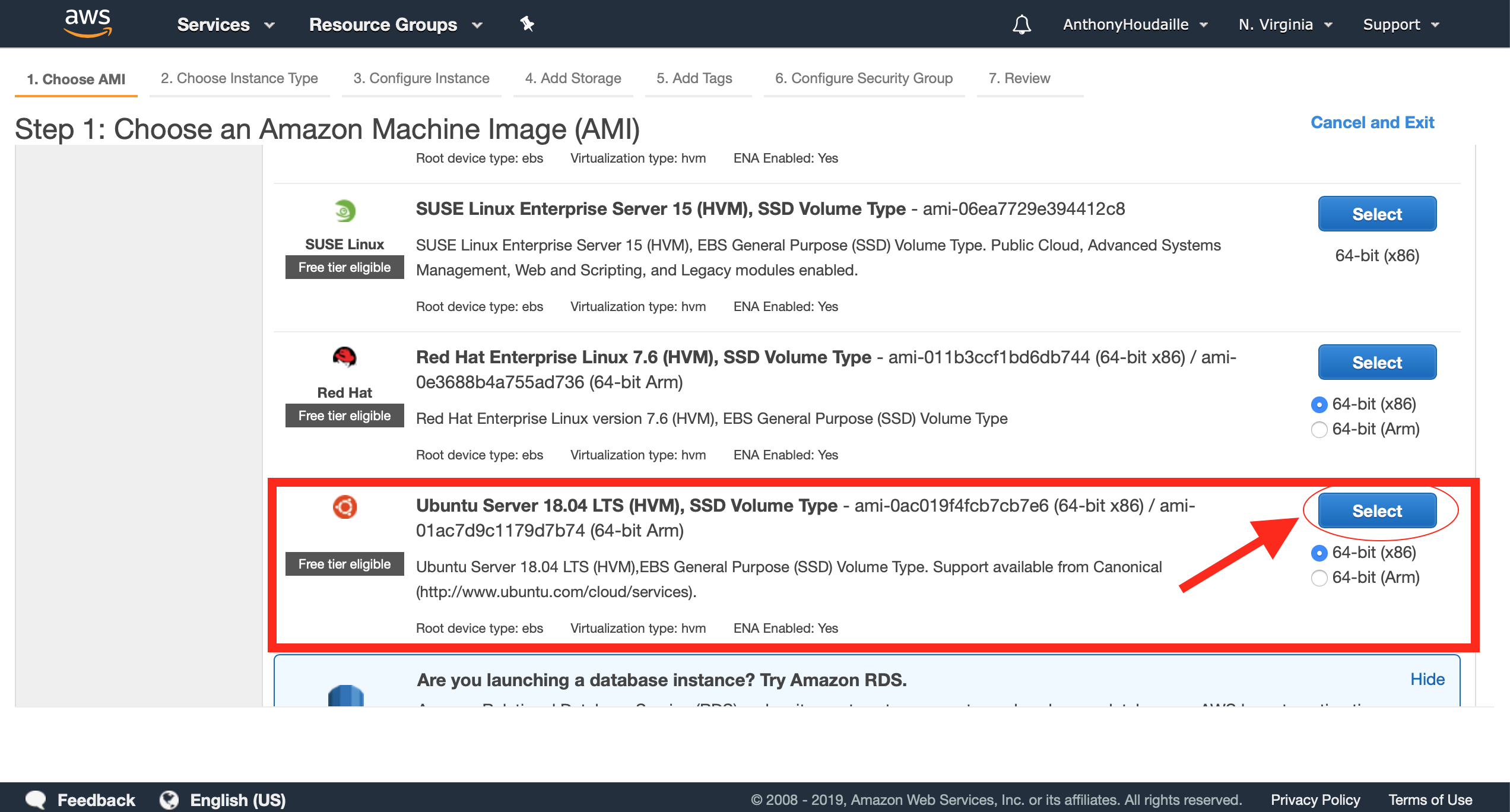
4. Instances options :
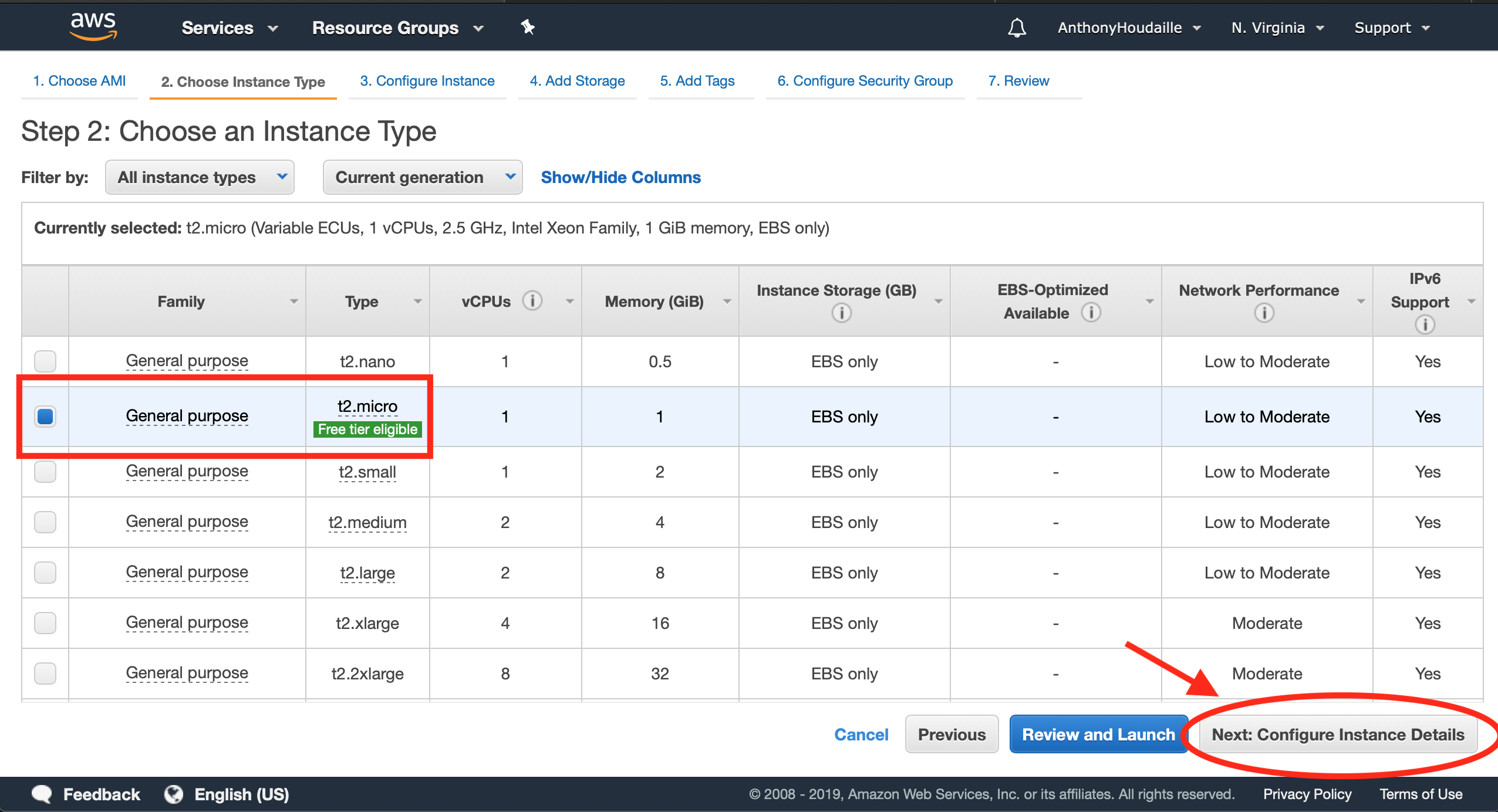
a. Select the type
Select the type of instance you would like to launch. Make sure to select an instance that matches your needs. t2-micro are perfect for test phases. When deploying services in production, you might want to focus on m5d.xlarge for example. Take a look at the following link for the detailed hourly cost of each machine : https://aws.amazon.com/fr/ec2/pricing/reserved-instances/pricing/
b. Configure your instance
Dependeing on the complexity of your project and the resiliency requirements, you might want to add several instances to your cluster. Here for example, we’ll add 8 instances. 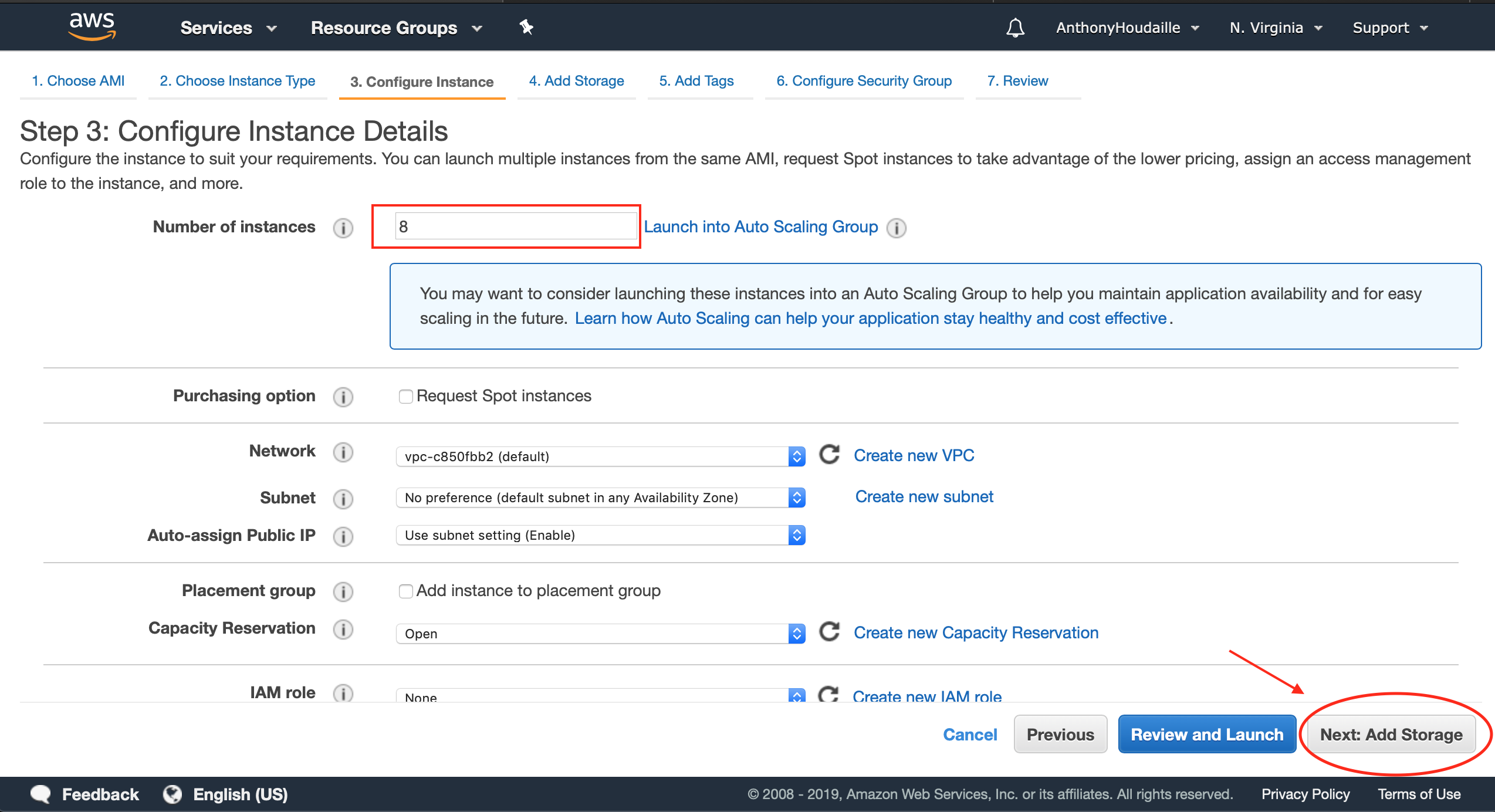
c. Add Storage
At the next step, you’ll be invited to add storage. Some Big Data projects imply several To. of data. For the sake of simplicity, we’ll use the standard storage of 8Gb. The storage is typically paid by Gb stored monthly. For exemple, in my GDELT progect , we needed 650GB on each instances.
d. Add Tags
If needed, add tags. Else, just move on to the next step.
e. Configure Security Group
The security group allows your instances to communicate with other instances within the same security group. The communication between the slaves and the master is essential to transfer data typically.
For example, if you create 2 instances. Then, 2 days later if you want to add some instances to your cluster, you must put your new intances under the same security group as the old ones.
This specific configuration allows SSH from anywhere. You might want to change this setting when working on real data. 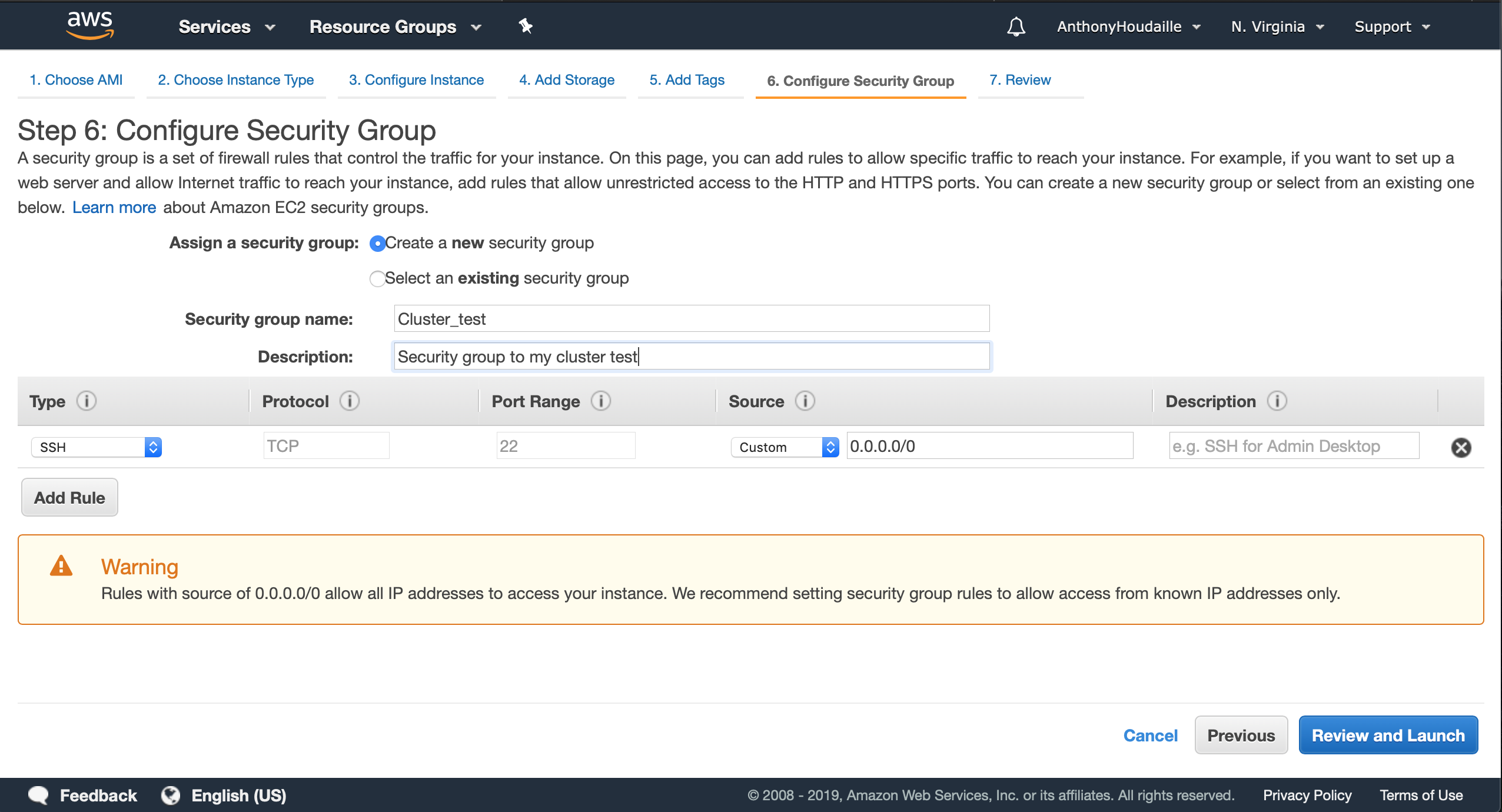
f. Review and launch
We’re almost done. Just review your previous step, and click “Launch”.
5. Create a Key Pair
“Amazon uses public–key cryptography to encrypt and decrypt login information. Public–key cryptography uses a public key to encrypt a piece of data, such as a password, then the recipient uses the private key to decrypt the data. The public and private keys are known as a key pair”. At this step, simply create a key pair and make sure to save it ! 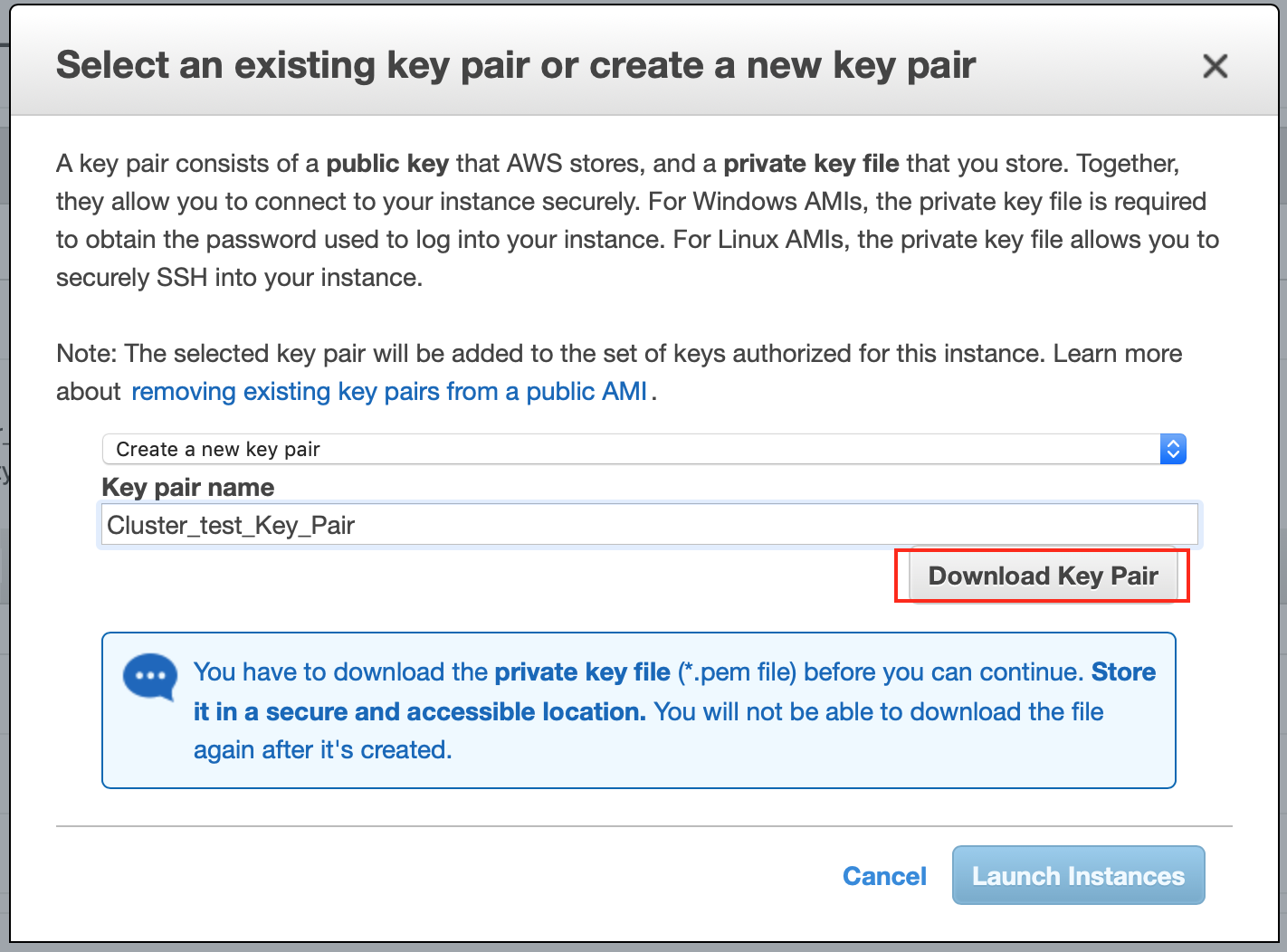
If you are working on Windows or Linux, I think the extension would be something like .txt. Make sure to change it to .pem to identify your file as a key pair.
6. Change the Name of your Intances
All your instances are now being initialized. For clarity, change the name of your instancess accoringly to their role. 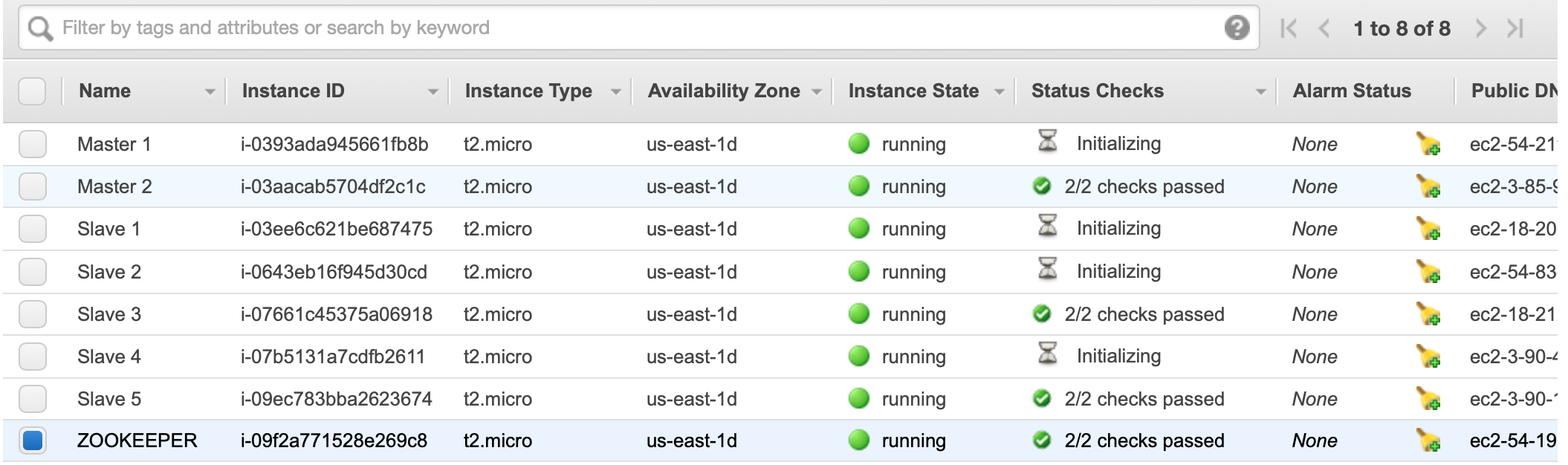
7. Connexion to our Instances in SSH
a. Protect your KeyPair against accidental overwriting
Open your terminal. Once you are in the folder that contains your key pair, copy-paste this code :
bash chmod 400 Cluster_test_Key_Pair.pem
b. Try a connexion to one of your instances
Copy the public DNS on AWS’ website : 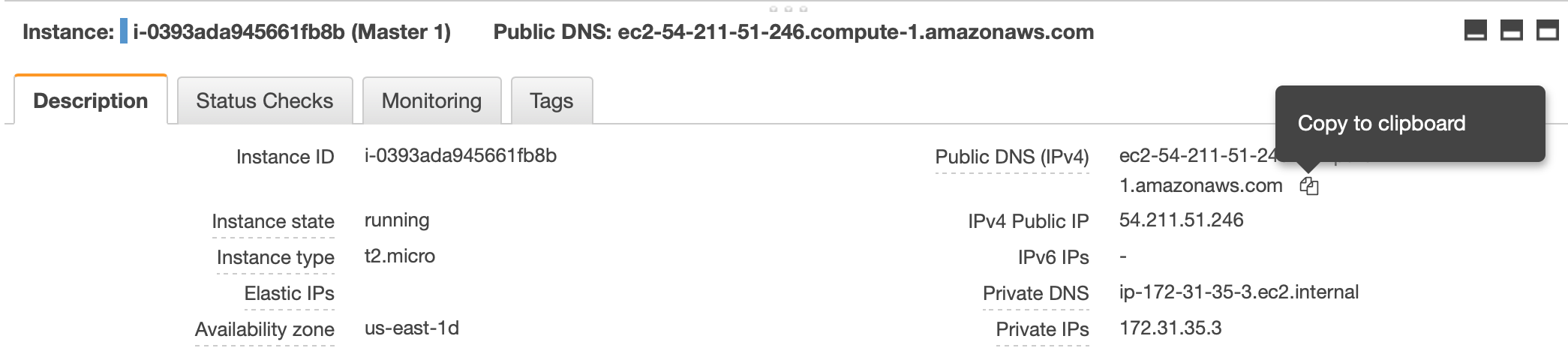
Then, go back to your terminal and execute the commande bellow :
ssh -i "<path to your keyPair directory>/Cluster_test_Key_Pair.pem" ubuntu@<copy the public DNS>
Example :
ssh -i "/Users/anthonyhoudaille/Desktop/Tuto_Cluster_EC2_AWS/Cluster_test_Key_Pair.pem" ubuntu@ec2-54-211-51-246.compute-1.amazonaws.com
Conclusion : Well done ! You’re connected to your instances in SSH.
You can pass to my new tutorial : How to Install Apache-Cassandra on AWS EC2 Instances
Thank you for reading.
If you have any questions, please, don’t hesitate to send me an email.
